| microscope base |
| microscope arm |
| microscope stage |
| microscope body tube |
| microscope condenser |
| microscope iris diaphragm |
| microscope revolving nosepiece |
| microscope obective lenses |
| microscope focal point |
| microscope coarse adjustment |
| microscope fine adjustment |
| microscope field of vision |
| microscope magnification |
| formula for magnification |
| resolution |
| refractive index |
| parfocal |
| which lens has the shortest focal distance? |
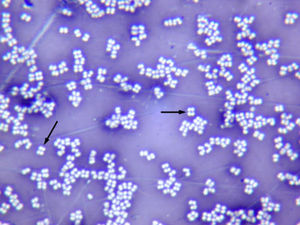
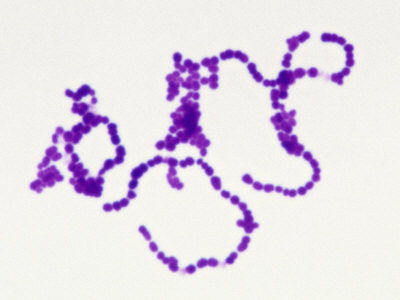
| the three basic bacterial shapes |
| the field of vision decreases when the magnification... |
| why does immersion oil increase resolution? |
| when viewing large organisms like fungi or protozoa, it is best to use the ___________ lens |
| spherical aberration |
| chromatic aberration |
| In bright field microscopy, the image is made from: |
| Bacterial stains will _____ the organism |
| The condenser lens ___________ the light |
| Refraction is ________ of light rays |
|
A microscope produces 2 images. One is _____ and one is ______. |
| The virtual image appears ___________ the microscope |
| The formula for calculating magnification: |
| Resolution is defined as: |
| The limit of resolution is: |
| Write the formula for the limit of resolution: |
| Numerical Aperture is: |
| Using immersion oil makes the numerical aperture__________ |
|
In dark-field microscopy, objects appear ________ against a _________ background |
| In phase contrast microscopy, the specimen appears as various levels of ______ against a bright background |
|
Fluorescent microscopy uses fluorescent ______ that emit light when illuminated with _____________ light |
| A mixed culture contains: |
| A pure culture contains: |
| The purpose of streaking bacteria on a plate is to: |
| Individual cells grow into: |
| CFU stands for: |
| A CFU consists of: |
| Ubiquitous: |
| Define pathogenic: |
| Define opportunistic pathogen |
| define reservoir: |
| Pellicle |
| sediment |
| turbidity |
| flocculent |
| Organisms that can infect us: |
| Organisms that may transmit disease |
| most commonly used staining method |
| gram staining - which stain is applied first? |
|
gram staining
what forms inside the cell after you add iodine?
|
|
gram staining
what type of cell is decolorized? |
|
gram staining
Name the counterstain |
| what effect does alcohol have on the gram-negative cell wall? |
| Explain why gram-positive cells are not decolorized |
| What color will gram-positive cells be if the decolorizer is left on too long? |
| Describe the appearance of a good emulsion |
| what happens to older gram-positive cultures? |
| In the negative staining technique a chromogen (dye) has a ____________ charge. |
| The pH of negative stains is_____________ |
| Negative stains do not enter bacterial cells because the charges ____________ each other. |
| Negative staining is commonly employed for bacteria that are: |
| Acid-fast bacteria have ____________ in their cell walls |
| Acid-fast organisms resist _________ by _________ alcohol. |
| The names of the 2 acid-fast staining procedures are: |
| When preparing an acid-fast smear, a drop of __________ is used to help the ____________ organisms adhere to the slide |
| The primary stain in the ZN method is _________ because it is soluble in _____________ |
| Heating causes acid-fast cell walls to _________ |
| the counterstain in an acid-fast stain is |
| Acid fast cells are colored |
| Non acid-fast cells are |
| Capsules are made of __________ or _________ |
| (Capsule stain) Two examples of netgaive stains are: |
| (Capsule stain) Negative stain pH is ___________ and they stain the background |
| (Capsule stain) A basic stain is used to stain _________ |
| (Capsule stain) We do not heat fix because: |
| Cells stick to the slide by adding a drop of ___________ |
| An endospore is: |
| Endospores are covered with a protein called: |
| (endospore stain) The primary stain is called: |
| (endospore stain) The decolorizer is: |
| (endospore stain) The cells that are counterstained with safranin are ______________ and _____________ |
| Location of endospore: central |
| Location of endospore: terminal |
| location of endospore: subterminal |
| Two spore shapres are: |
| some spores are large and make the cell look: |
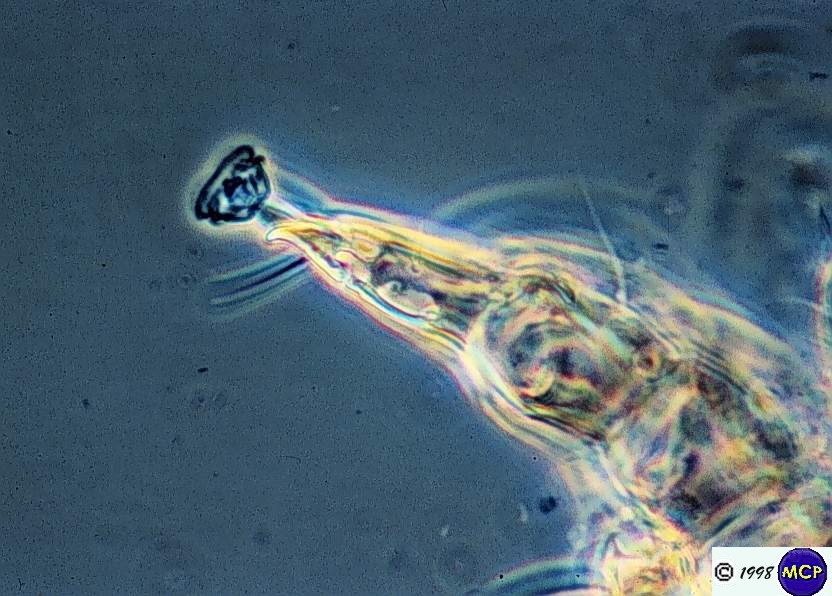
| Why can't we view flagella using an unstained preperation? |
| flagella - monotrichous |
| flagella - amphitrichous |
| lophotrichous |
| peritrichous |
| Why does light of a shorter wavelength produce a clearer image than light of longer wavelengths? |
| Colony morphology includes: |
| colony morphology - shape |
| colony morphology - margin |
| colony morphology - elevation |
| colony morphology - texture |
| colony morphology - color |
| colony morphology - other factors |
| Why are microorganisms located on the desks not sterilized as extremely as the plates? |
| What is significant about organisms that grow well at 37 degrees C? |
| Capsule stain - why must the sample be emulsified in serum? |
| Why do oral bacteria produce a capsule? |
| Why was an older culture of Bacillus used to demonstrate endospores? |
| Why can't flagella be observed in action? |
|
Type of microscopy:
|
|
Type of microscopy:
|
|
type of microscopy:
|
|
type of microscopy:
|
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology
|
|
bacterial morphology
|
|
bacterial morphology
|
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology: |
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology:
|
|
bacterial morphology
|
| How to do a plate streak: |
|
Broth growth:
|
| Gram stain procedure |
|
gram positive vs gram negative results:
|
|
Negative stain:
|
|
acid-fast stain (ZN)
|
|
acid fast stain (K)
|
|
capsule stain:
|
|
Flagella stain:
|
|
flagella:
|
|
flagella: |
|
flagella:
|
|
Endospores:
|
|
endospores
|