| Explain the difference between an acute injury and a chronic injury |
| An acute injury has a sudden onset due to a specific trauma such as twisting the your ankle. A chronic injury is when excessive repeated stress is placed on one area of the body over an extended period of time. |
| RICE |
| Rest Ice Compression and Elevation |
| supine |
| lying face up |
| Where does this chronic injury occurs most often Chondromalacia Patella |
| Knee Cap |
| Shin splints |
| pain occurring in the anterior or lateral lower leg |
| Anterior compartment syndrome |
| very common injury in running it is a condition involving the three muscles in the anterior of the leg |
| Which are the three muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg |
| Tibialis anterior, extensor hallucus longus and extensor digitorium longus |
| is a term used for generalizing pain and or tenderness in the metatarsals, the heads of the long bone in the foot |
| Metatarsalgia |
| List the part of the body in which plantar fasciitis occurs |
| bottom surface of the arch of the foot, pain commonly generates near the heel and progresses towards the ball of the foot. |
| Tendinitis |
| is inflammation of the connectivity tissues that joins a muscle to a bone |
| A Sprain |
| is a tearing or overstretching of a ligament. |
| Liagament |
| is a connective tissue that connects bone to bone and reinforces joints from dislocating |
| Strain |
| is a over stretching or tearing of a muscle tendon |
| Where does this chronic injury occurs most often: Achilles Tendonitis |
| In the calf muscles |
| What is the difference between a muscle sprain and a muscle strain |
|
A sprain is a tearing or over stretching of a ligament
A muscle strain is a over stretching or a tearing of a muscle tendon |
| what is the First aid action for a Musculoskeletal injury |
| Rest Ice Compression and Elevation (RICE) |
| CAD |
| Coronary Artery Disease |
| Advance stages of heat exhaustion may lead to |
| Coma |
| in order to avoid dehydration during exercise and prevent heat exhaustion, an individual should |
| monitor hydration levels |
| to ensure proper hydration during exercise how many ounces of fluid should you consume shortly before exercise |
| 8 - 12 onces |
| Name an activity that utilizes the aerobic energy system |
| Indoor cycling |
| To promote and maintain health, an individual should perform how many minutes and days per week of moderate intensity physical activities |
| 30 minutes 5 days per week |
| One way to determine an individual's estimated maximal heart rate is |
| to subtract his / her age from 220 |
| Name two atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseas risk factors that will improve by regular participation of physical activity |
| Blood pressure and total serum cholesterol |
| The system that allows the blood to flow through the heart, lungs and body is called |
| The circulatory system |
| A basic function of of the bone that make up the skeletal system is to |
| Provide a site for the production of red blood cells |
| what method is known as variable intensity or spontaneous training |
| intermittent training |
| The primary muscles performing work are called ______________ and may be identified by a specific ____________ |
| Agonist , joint action |
| Movement of the hip include ___________ and _________joint action |
| abduction , adduction |
| Advance stages of heat exhaustion can lead to |
| Coma |
| List 4 steps in recognizing an emergency |
| Survey, assessment, prioritization,implementation (SAPI) |
| Indoor cycling utilizes which energy system |
| aerobic energy system |
| What is the Cardiovascular system |
| The system that allows the blood to flow through the heart, lungs, and body |
| The ____________ method is known as variable intensity or spontaneous training |
| intermittent |
| List 8 health benefits associated with regular participation in physical activities |
| Lower risk of early death, stroke,Breast cancer, high blood pressure,colon cancer,prevention of Weight gain, muscular fitness, improved cardio respiratory |
| How can interval training improve aerobic performance |
| it increases aerobic endurance and anaerobic power It maximizes aerobic power especially for athletes training to compete |
| Define energy and its food source |
|
Energy is the ability to work Food source is plants and animals |
| Define ATP |
|
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Intracellular carrier of chemical energy produced by the body for muscular work |
| List the 3 physiological adaptions that occur to improve exercise performance and state how or why improvement occurs |
|
1. Increased maximal blood flow - The hart pumps more blood with each beat and increases stroke volume
2. Increased oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide removal this allows athletes to posses high pulmonary ventilation during maximal aerobic exercise
3.Increased maximal oxygen uptake and aerobic power
4.Increased blood flow and increased capacity and power of the aerobic system |
|
Anaerobic path way ATP - CP / Phosphagen system: Fuel source,Intensity, Duration
|
|
creatine phosphate intensity- very high very short 15-20 sec
|
|
Lactic acid system 1- fuel source- 2-intensity 3- duration- 4- list 3 examples of activities that utilize this system- |
|
carbohydrates only high/moderate 3- duration- short/medium
prolonged sprints, swimming, cycling Weight training |
| List 3 examples that utilizes the anaerobic - lactic acid system |
| Sprinting, jumping, kicking |
| Name the energy pathways |
| Anaerobic pathway, Lactic Acid system, Aerobic pathway |
| Name the Aerobic pathway |
| Aerobic system |
|
name the Aerobic systems: Fuel Source, Intensity, Duration
|
|
Carbohydrates, fats , proteins Low to moderate 40 to 60 minutes low intensity long duration
|
| List 3 activities that utilizes the Aerobic system |
| Sitting, Sleeping , resting, walking |
| Aerobic |
| Literally with oxygen or in the presence of oxygen |
| Anaerobic |
| Requiring no oxygen usually short spurt high energy activities |
| Steady State |
| after the first 3 - 4 minutes of exercise oxygen uptake has reached an adequate level to meet the oxygen demand of the tissues |
| List the 4 steps in recognizing an emergency |
| (SAPI) Survey, Assessment, Prioritization, Implementation |
| FITT Principle: training variables |
|
Frequency: number of exercise sessions per week
Intensity: difficulty of an exercise or exercise session
Time:duration or length of each exercise session
Type: the mode of activity performed |
| Describe the principal of overload |
|
To achieve desired training improvements or effects the relevant body system must be overloaded beyond its normal level of capacity.
Fitness programs that lack overload or variation will serve to maintain and not improve one's existing level of fitness. |
| Instructors should evaluate an exercise from which two view points |
|
Effectiveness (benefits) and potential risk (injury quotient) |
| AFAA 5 questions |
|
1.What is the purpose of this exercise
2.Are you doing that effectively
3.Does the exercise create any safety concerns
4.Can you maintain proper alignment and form for the duration of the exercise
5.For whom is the exercise appropriate or inappropriate |
| According to Afaa , a group exercise instructor should teach at what level |
|
At a intermediate level
explain and/ or demonstrate modifications
to achieve more or less intensity variations
|
| List the definition, purpose,and duration of a FINAL CLASS SEGMENT |
|
Definition: the final class segment is the closure of a workout in which stretching and or relaxation and stress reducing techniques can be included.
Purpose: is to decrease heart rate and blood pressure, relax the muscles and physiological stress.
Duration:depending on the instructors class design typically it is 5 - 10 min |
| List and describe 3 common relaxation methods |
|
Physical focus: method focuses on the bodily system and sensations in attempt to increase relaxation Mentally
Abstract focus: uses imagination to create a sense of relaxation.
Combination focus: combines booth Physical focus and Mental focus to achieve a greater relaxation response. |
| list special considerations for a final class segment. |
|
Heart rate monitoring
Saunas and hot tubs Method selection |
| A training variable that should be considered when designing an exercise program: |
| Frequency |
| The Karvonen formula incorporates the ------------ in determining the training heart rate range (THRR) |
| resting heart rate |
| A warm - up is the _________ period for a specific workout |
| preparation |
| Movements of the hip include _____ and ____joints action |
| abduction and adduction |
| The definition of _________ is when oxygen uptake has reached an adequate level to meet the oxygen demand of the body |
| steady state |
| A skill - related component of physical fitness is: |
| Coordination |
| In order to safely perform full range of motion during cardio hi/low-impact class, beats per minute (bpm) should range between --- and --- |
| 130 and 155 bpm |
| In a push - up, the ____ muscles extend the elbow and the ______ adducts the humerus to lift the body up against gravity |
|
Triceps
and
Pectoralis major |
| Which type of muscle contractions (also referred to as muscle action) does not require the muscle to change length when exerted against a fixed resistance |
| Isometric |
| A multi - joint exercise that utilizes the gluteus maximus and hamstrings |
| Lunge |
| Which type of connective tissue connects bone to bone |
| ligament |
| The function of ______ is to sense the degree of tension and the length of the muscle |
| propriocepters |
| To enhance flexibility during the end of class cool down segment , the AFAA recommends performing______ stretches for _______ seconds |
| Static , 15-60 |
| Besides heart rate monitoring, another method of measuring exercise intensity is |
| Perceived exertion |
| In order to teach a quality group exercise class and instructor should be able to |
| apply the AFAA 5 questions |
| A variable that acts as a determinant of exercise behavior is |
| cultural values |
|
To maintain proper alignment , particular attention should be given to ___ in the standing position |
| holding a neutral pelvic alignment |
| Lordosis is associated with an anterior tilt of the pelvis, and may be a result of |
| Weak abdominals |
| Kyphosis or excessive curvature of the thoracic spine may be the result of |
| Osteoporosis |
| a movement that performs shoulder horizontal abduction is |
| High Row |
| advance stages of heat exhaustion may lead to |
| Coma |
| In order to avoid dehydration during exercise and prevent heat exhaustion, an individual should |
| monitor hydration levels |
| A motivational technique called ___ is used to sustain a type b participant for life long exercise adherence |
| Acknowledgement |
| One purpose of the final cool - down phase of an aerobic exercise session is to |
| prevent blood pooling |
| Which condition is referred to as an overuse injury |
| Tendinitis |
| The 1996 US surgeon general's report on Physical Activity and Health was a call to |
| encourage more Americans to become active |
| The AFAA recommends checking the pulse at the _____artery |
| Radial artery |
| One way to increase exercise intensity is to |
| add traveling |
| The AFAA recommends that a recovery heart rate be taken _____ of aerobic work |
| 3 - 5 minutes upon conclusion |
| a food, such as ______ represents a complete source of protein |
| poultry |
| If an individual's training workload for muscular strength and / or endurance is discontinued, a reduction in muscular fitness may occur after _______ months |
| 3 months |
| According to the AFAA FITT at a glance , participants should aim for a cardio respiratory exercise intensity that burns a minimum of ______ kilo calories per week |
| 1000 |
| Improvement in cardiorespiratory fitness can be attained with a minimum intensity of _____% of heart rate reserve (HRR) |
| 40% |
| Flexibility can be achieved by stretching to the end range of motion or: |
| point of tightness |
| When performing a squat, during the concentric contraction _____ occurs |
| hip extension |
| Training in water encourages freedom of movement without the fear of falling due to |
| Bouyancy |
| Because speed is used to increase resistance , water is also an effective modality for _________ training |
| Power |
| In Mat Science, the principle of ___________ refers to exercise selection |
| Progression |
| When introducing varying road situations in an indoor cycling class, be sure that there are _______ transition movements and changing terrain |
| smooth |
| For individuals to receive an efficient and challenging form of conditioning that works well for developing muscular strength and endurance, cardiovascular endurance, stability, balance and coordination they should participate in ___________ training |
| Circuit |
| The explosive aspect of strength defines muscle? |
| Power |
| What form of exercise is designed to achieve maximum muscular involvement? |
| variable resistance |
| A push up works the pectoral muscles, anterior deltoids and the ________ |
| triceps |
| Early recognition of a medical emergency can be summarized into the SAPI approach the S stands for |
| Survey |
| Response to an acute injury includes |
| elevation |
| The AFAA 5 questions: |
| Evaluate the risk of exercise |
| The purpose of torso stabilization training is to: |
| enhance ability to maintain proper spinal alignment |
| an example of a basic exercise position is |
| prone |
| when considering correct alignment while moving, instructors should make sure participants |
| control the ROM with movement |
| an appropriate alignment cue for hands and knees position |
| Hands directly under the shoulders |
| The AFAA recommends that _______ be incorporated within the warm -up portion of the class |
| movement rehearsal |
| A danger sign of exercise is |
| breathlessness |
| Correct standing alignment includes the pelvis in a / an_________ |
| Neutral position |
| Time bouts of increased intensity work followed by lower intensity recovery is known as _______ training |
| interval |
| A method for improving the muscular strength and endurance would be ______ training |
| multi joint |
| Instructors should make sure that participants keep hands relaxed when gripping weights in order |
| avoid performing the Valsalva maneuver |
| When working with participants diagnosed with asthma, instructors should allow for _______ and ______ |
| an extended warm up and cool down |
| To assist in the management of arthritis, participants should be encouraged to ______ daily |
| Stretch |
| a probable cause of common injuries associated with group exercise classes may be : |
| body mechanics |
| Music is commonly written in a standard ___ beat |
| 4/4 beat |
| If a participant complains about pain that has been persistent over the past few weeks, an instructor should |
| recommend a physician's evaluation |
| In traditional dance choreography, movements should include ____ as of one of its basic elements |
| motivation |
| Based on research ____________ components have resulted in improved performance in daily activities for older adults. |
| Skill related |
| To ensure proper hydration during an exercise session, participants should monitor hydration levels and consume _____ ounces of fluid shortly before exercises |
| 8 - 12 ounces |
| When working the deltoids, which joint action is performed at he shoulder |
| Flexion |
| when flexing the hips in a standing position, the back should |
| maintain neutral alignment |
| Traditionally known as oxygen dept, refers to oxygen uptake remaining elevated above resting levels for several minutes during exercise recovery is called: |
| EPOC ( Excess post Oxygen Consumption) |
| a period in which the level of oxygen consumption is below what is necessary to supply appropriate ATP production required of any exercise is called___ |
| Oxygen deficit |
| The point at which the body can no longer meet its demands for oxygen and anaerobic metabolism is accelerated is called _______ |
| Anaerobic Threshold |
| The ability of the body to remove oxygen from the air and transfer it through the lungs and blood to the working muscles: related to cardio respiratory endurance: -------- |
| Aerobic capacity |
| The by product of anaerobic metabolism of glucose or glycogen in muscle is called _____ |
| Lactic acid |
| The volume of blood ejected by each ventricle of the heart during a single systole is called ______ |
| Stroke volume |
| The volume of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute is called ______ |
| Cardiac Output |
| The pumping action of the muscle in the extremities and respiratory system along with venoconstriction to move oxygen poor blood back to the heart is called ___ |
| venous return |
| The pressure of the blood in the arteries is called |
| Blood pressure |
| a condition caused by ceasing vigorousley exercise too abruptly so that blood remains in the extremities and may not be delivered quickly enough to the hart and brain is called _____ |
| Blood pooling |
| The greatest volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled after the deepest inspiration is called_____ |
| Vital capacity |
| a dangerous condition that occur if an individual hold his her breath, causing the glottis to close the stomach muscles to contract, forming an on equal pressure in the chest cavity, reduced blood flow to the hart and insufficient oxygen supply to the brain is called ___ |
| Valsalva maneuver |
| _________ are the point at which two or ore bones meet articulate and where movement occurs |
| Joint |
| Bands of sheet like fibrous tissues that connect bone to bone and reinforce joints from dislocation they are nonelastic and have limited range of motion |
| Ligaments |
| Band of dense fibrous tissue forming the termination of a muscle and attaching muscle to bone with a minimum of elasticity is called___ |
| A tendon |
| White semi opaque fibrous connective tissue cushions and prevents wear on articular surfaces is called ______ |
| Cartilage |
| Anatomical term for Anterior |
| To the front |
| Anatomical term for Posterior |
| to the back |
| Anatomical term for Supine |
| lying face up |
| Anatomical term for Medial |
| Toward the midline of the body |
| Anatomical term for Lateral |
| side to side away from the midline |
| Anatomical term for prone |
| lying face down |
| Anatomical term for suprior |
| above or the upper half of the body |
| Anatomical term for Inferior |
| below or the lower half of the body |
| Anatomical term for unilateral |
| affects only one side of the body |
| Anatomical term for bilateral |
| affects booth side of the body equally |
| horizontal plane ( transverse) |
|
Plane that devides the body into upper and lower halves |
| sigittal plane |
| Plane that divides the body into right and left is |
| frontal plane |
| a plane vertical to the median line that divides the body into anterior and posterior |
| Flexion |
|
Bending of a joint between two bones that decreases the angle between the two bones |
|
extension
|
|
A motion of increasing the angle between two bones straightening of a muscle previously bent in flexion
|
|
abduction
|
| Movement away from the midline |
|
adduction
|
| movement toward the midline |
|
Rotation
|
| movement around the axis |
| circumduction |
|
movement in which the extremity describes a 360 degree circle |
|
agonist
|
| A muscle that is a prime mover, directly responsible for a particular action |
|
antagonist
|
| A muscle that acts in opposition to the action produced by a prime mover |
|
primary movers
|
| a muscle directly responsible for a particular agonist action |
|
assistors
|
| A muscle that helps perform the same task |
|
Stabilizers
|
| muscle that helps prevent undesired or unnecessary motion |
|
isometric contraction
|
| A muscle contraction in which the tension increases but muscle length remains the same |
|
Concentric Contraction
|
| Muscle shortens as positive work is done against gravity |
|
Eccentric contraction
|
| Muscle Lengthens while contracting,developing tension as when the muscle oppose the force of gravity is |
|
Isotonic contraction
|
| A muscle contraction in which the tension remains constant as the muscle shortens or lengthens is called |
| Fast twitch muscle fibers are ___ |
| able to generate quick, high -intensity contractions |
| Name three postural deviations of the back |
| Cervical , Thoracic, Lumbar |
| List six classes of nutrients |
| Water Fat Carbohydrates Vitamins Protein Minerals |
| What are vitamins? |
| Vitamins are non - caloric, organic compounds needed in small quantities to assist in such functions as growth maintenance and repair. |
| which body part does this chronic injury occurs most often Plantar Fascist |
| Bottom surface of the arch of the foot |
| Which body part does this chronic injury occurs most often chondromalacia |
| Knee Cap (Patella) |
| which body part does this chronic injury occurs most often Achilles tendonitis |
| Calf muscles |
| Specificity of training principal (SAID) stands for |
| Specific Adaption To Imposed Demand |
| Describe SAID |
| training must be relative to the activity for physiological change to take place. |
| Describe reversibility principal |
| If one's training workload is decreased, physical fitness will also decrease |
| Growths that develop on the vocal cords due to overuse injury, resulting in severe chronic hoarseness. |
| Vocal Nodules |
| Describe Principal of over training |
| The body needs to recover and musculoskeletal system needs time to rebuild from the stress of vigorous exercise. |
| List the health related components of physical fitness |
|
Cardio respiratory fitness Muscular Strength and endurance Flexibility Body Composition |
| List the skill related components of physical fitness |
|
Agility
Balance
Coordination
Power
Reaction
Time
Speed |
| Which other organization's training recommendations does AFAA support |
| The ACSM American College of Sports Medecine |
| define Par - Q |
|
Physical Activity Readiness Questionaire
a written procedure used by fitness facilities regarding participating screening |
|
Name the 6 classes of nutrients
|
|
Water Carbohydrates Protein Fat Vitamins Minerals
|
|
RDA
|
|
The recommended dietary allowance
|
|
DRI
|
|
Dietary reference intake
|
|
Name the functions of water consumption in our bodies
|
|
Water acts as a transport medium for nutrients
Aids in digestion and elimination
Directly maintains body temperature
Adequate functioning of immune system and brain
|
|
Lack of water can cause disorders such as
|
|
Difficulty concentrating
Dizziness
Muscle spasms
Failing kidney function
|
|
List the diffrent types of carbohydrates |
|
Fiber rich foods, vegetables and whole grains
|
|
What are vitamins
|
|
non caloric , organic compounds needed in small quantities to assist in such functions as growth maintenance and repair.
|
|
Describe the difference between fat soluble vitamins and water soluble vitamins
|
|
Fat soluble A,D,E and K can be stored by the liver overdosing may lead to toxic levels in the body
Water soluble C and B6 is excreted by the kidney when taken in excess
|
|
What are minerals
|
|
are inorganic compounds that assist processes, such as regulating activity of many enzymes an maintaining acid—base balance and are structural constituents of body tissues Iron - red bood cells Calcium- bone and teeth |
|
List 8 dietary guidelines for Americans outlined by the US department of health and human services and U.S department of agriculture
|
|
Adequate nutrition
Alcoholic beverages
|
|
Describe my pyramid and how participants benefit from this resource
|
|
offers personalized eating plans and interactive tools to help you plan/access food choices based on dietary guidelines for Americans. it will help give participants better understanding of what to eat and how much exercise to maintain a healthy lifestyle
|
|
What is AFAA's nutritional supplement policy and discuss what the role and responsibilities of a fitness professional are when it comes to the sale and distribution of nutritional supplements
|
|
only can be sold under MY name, where item is sold in good faith to only good candidates
|
|
Explain the difference between an acute injury and a chronic injury
|
|
Acute injury sudden onset due to a specific trauma Chronic injury most common, long term
|
|
Plantar fasciitis
|
|
inflammation of fascia/connective tissue of the plantar or bottom surface of the arch of he foot
|
|
Chondromalacia
|
|
overuse injury affecting a articular cartilage of the posterior surface of the patella or knee cap
Common symptoms: Generalizing pain that tends to increase with weight bearing knee flexion activities such as squats , walking up and down stairs or sitting for a long period with bent knees.
|
|
Archilles tendonitis
|
|
inflammation of connective tissue that joins muscle to bone
|
|
What is the difference between a muscle strain and muscle sprain
|
|
strain- overstretching or tearing of a muscle or tendon
|
|
list 3 ways to prevent voice nodules
|
|
Correct posture |
|
list 3 ways to prevent low back pain
|
|
proper positioning of hip flextors Proper positioning of knees and spine
|
| list 3 ways to prevent shin splints |
|
proper footwear Proper flooring Warm up properly
|
|
4 things that may contribute to heat injuries, cardiovascular conditions, or exercise induced conditions as they relate to participation in physical activity
|
|
dehydration
|
|
FITT principal
|
|
Frequency : refers to the number of exercise sessions
Time: refers to the duration or length of each exercise session
|
|
Will one FITT variable effect the other ? How? Give an example? |
|
Yes Exercise intensity will decrease duration of the exercise session Different exercises apply different stress on the body so all can not be done at the same intensity
|
|
Principle of overload
|
|
to achieve desired training improvement /effect the body must be overloaded beyond its normal level or present capacities
|
|
principal of progression |
|
exercise program should provide gradual increases or (a systemic change) in frequency/intensity/time/type conditioning phase 4-6 weeks Improvement phase 4-5 months And maintenance there after
|
|
Specificity of training principal (SAID)
|
|
Specific
|
|
Reversibility principle
|
|
If workload is discontinued or decreased, detraining in performance will occur
Cardiovascular fitness decreases after 2 or 3 weeks without training
Muscular fitness ( strength endurance )deceases after 2-3 months without training
|
|
Principle of overtraining
|
|
The body needs time to recover & musculoskeletal system needs time to rebuild from the stress of vigorous exercise.
Without sufficient rest, overtraining occurs
Overtraining can also occur when training volume and / or intensity are too high or too rapidly increased
|
|
List health related components of physical fitness
|
|
Cardio respiratory fitness
|
|
List skill related components of physical fitness |
|
Agility - ability to change the body’s position direction with quickness and accuracy
|
|
Outline the 2008 physical activity guidelines for Americans which reinforced the 1996 US Surgeon General's report on physical activity and health
|
|
· should avoid inactivity - some activity is better than none ·
intensity aerobic activity or 150 minutes a week of vigorous activity strengthening activities including all major muscle groups 2 or more days a week these activities provided additional health benefits are gained
|
|
Which other organization's training recommendations does AFAA support?
|
|
American College of sports medicine (ACSM)
|
|
What does BMI stand for and what measurement constitutes an individual to be defined as obese?
|
|
Body Max Index > 30 % is considered Obese
|
|
Professional responsibilities may include what 7 items
|
|
Personal liability coverage
|
|
Par-Q
|
|
PAR –Q Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire
|
|
Medical clearance recommendation for high-risk participants
|
|
men & women of any age, with 1 major cardiovascular ,pulmonary or metabolic disease signs or symptoms
Requirements :Medical exam medical clearance & exercise testing before participating In moderate- vigorous exercise
|
|
Medical clearance recommendation for moderate risk participants
|
|
Men & women, ≥ 2 atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors but without symptoms Requirements :Medical exam and clearance before participating in vigorous exercise
|
|
Medical clearance recommendation for low risk participants
|
|
Men & women who are without symptoms and have ≥ 1 CVD risk factor
-Most instances do not require medical clearance before participating in vigorous exercise
|
|
List 10 exercise danger signs (participants should STOP exercise and instructor should assess the need for emergency response procedures)
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting - dizziness/unusual fatigue
Tightness or pain in the chest
-loss of muscle control/ staggering
-severe breathlessness/ gasping
|
|
list 5 signs or participant complaints that would require exercise modification or cessation of exercise until signs disappear
|
|
Labored breathing
|
|
what should an instructor know about the effects of drugs and/or medications on exercise response
|
|
certain prescriptions/nonprescribed medications may elicit side effects during exercise
Individuals should consult their doctor before beginning an exercise program
|
|
list 6 symptoms of overtraining
|
|
Fatigue
Constant muscle or joint soreness on effort or motion, leaning toward pain
|
|
list 6 AFAA recommendations to avoid overtraining
|
|
1. vary class type/intensity warrant
|
|
In terns of hydration and rehydration .AFAA recommends : |
|
Hydrate before 8-12 oz of fluids shortly before class Hydrate during, and after exercise
|
|
Describe appropriate exercise attire the AFAA recommends
|
|
Fabrics that breath, comfortable clothing, shoes with proper design, support and cushioning
|
|
According to AFAA a group exercise instructor should generally teach at what class level?
|
|
Intermediate with explanation how to modify
|
|
Instructors should evaluate exercise from which two viewpoints _____________________ and ____________________
|
|
effectiveness and potential risk
|
| Exact wording of AFAA 5 questions |
|
What is the purpose of this exercise?
Are you doing that effectively? Does the exercise create any safety concerns? For whom is the exercise appropriate or inappropriate?
|
|
AFAA recommends that every group exercise class include:
|
|
Pre-class announcements
|
|
List definition, purpose, and duration of a proper warm-up
|
|
Defenition : is the preparation period for a specific workout
|
|
List and describe the 2 common warm-up methods and discuss when the addition of preparatory stretches may be appropriate
|
|
Movement rehearsal- lighter or less intense versions of movement ( low kicks , marching, ) goal is to increase Blood flow
|
|
list several special considerations for a warm up
|
|
intensity/impact, speed/control, ROM, sequence, spinal issues
|
|
List the definition, purpose, and duration of proper cardio respiratory training
|
|
Definition: to utilize continuous, rhythmical aerobic activities that target the large muscles to create increased demand for oxygen systems
|
|
list and describe 4 common cardio respiratory training methods
|
|
-continuous or stead training: gradually increasing intensity then gradually decrease
station or sequential manner
|
|
list several special considerations for cardio respiratory training
|
|
monitoring intensity
|
|
list the definition, purpose, and duration of proper muscular strength and endurance training
|
|
Definition: involves working individual or groups of muscles against a resistance to the point of muscle fatigue
activities ,increase muscle mass, increase metabolism, stronger bones, decreased risk of injury, improved posture/symmetry, and improved athletic performance
|
|
list and describe 4 common muscular strength and endurance training methods
|
|
Concentric– occurs when muscle tension is sufficient to overcome resistance and moves a body segment of one attachment toward the segment of its other attachtment
|
|
List special considerations for muscular strength and endurance training
|
|
Muscle balance ROM Speed and control Intensity Torso stabilization exercise Resistance equipment techniques Muscle conditioning exercise in the water
|
|
list the definition purpose and duration of proper flexibility training
|
|
Defenition: focuses on joint mobility and muscle suppleness/flexibility, and trhe reduction of muscular tension
|
|
list and describe three common flexibility training methods
|
|
Static stretches: involves placing targeted muscles in a elongated position and holding that position recommended 1-4 repetitions for each stretch hold for 15-60 seconds
These stretches can range from in intensity from a controlled , limbering movement to a ballistic force full one
involve an active contraction of muscle prior to stretch (often referred to as contract and release method)
|
|
list several special considerations for flexibility training
|
|
Intensity, Speed & control, ROM, Body temperatures
|
|
List the definition, purpose, and duration of a proper final class segment
|
|
Definition : closure of workout, which includes stretching, relaxation and stress reducing techniques
Duration typically 5-10 minutes
|
|
list and describe three common relaxation methods
|
|
physical- focuses on bodily systems and sensations as effort to increase relaxation
Relaxation
|
|
list several special considerations for a final class segment
|
|
Heart rate monitoring
Saunas and hot tubs
Method selection
Breathing (physical focus or combined focus)
The contract and relax method ( Physical focus)
Visualization (Mental Focus)
|
|
Explain resting heart rate (RHR)
|
|
Resting heart rate (RHR) refers to the number of times your heart beats in one minute while at rest.
|
|
How does increase cardio respiratory fitness affect RHR
|
|
The more conditioned your body is, the less effort is needed to pump blood through the body
|
|
How do THRR and HRR differ
|
|
THRR- maximum heart rate
|
|
explain recovery heart rate
|
|
Speed at which heart rate returns to pre-exercise level, indicator of sufficient cool down period
|
|
The preferred anatomical site for pulse checking is _______ secondary is _______
|
|
radial and Carotid
|
|
The AFAA recommended counting time for heart rate is ____ seconds
Once cued to begin , start counting beats with the number |
|
10 seconds
1
|
|
Rating of perceived exertion (RPE)
|
|
how hard individual feels they are working (1-10)
|
|
Talk Test
|
|
engaging in conversation during exercise represents work at near a steady state
|
|
Abruptly stopping cardio respiratory exercise affects exercise response how?
|
|
Can cause blood pooling
|
|
Working above target heart rate affects exercise response how?
|
|
you’re working anaerobically (without oxygen) and inefficiently, which is also too intense for many people, especially beginners
|
|
Stimulants
|
|
Gives you energy
|
|
Cardiac medications ( Beta blockers etc)
|
|
Will blunt the increase in heart rate and blood pressure , protecting the client from risk for exercise induced ischemia
|
|
Pressor response ( can result from many arm movements above the head)
|
|
The heart rate and blood pressure are elevated disproportionately to the oxygen cost of the activity
|
|
How would you define 'rhythm'
|
|
measuring motion w/ regular recurrence of elements or features- such as the beat of the music
|
|
What is meant by musical phrase
|
|
music grouped into 32 beats, keeps movements corresponding to beats
|
|
what are legal considerations when purchasing or creating music for group exercise
|
|
Music must be legally approved by performing rights
|
|
Define LIA, MIA, and HIA- explain how they differ
|
|
LIA- low impact aerobics, keep 1 foot on/close to floor
|
|
To lessen injury risk and maintain motivation in type A participants list 3 types of workouts that can provide different mechanical stresses to the body while allowing high intensity options for advanced training.
|
|
Step training, Kickboxing,Cycling
|
|
List 4 motivation techniques to sustain a type B participant for lifelong adherence.
|
|
Feedback, Support, Recognition, Encouragement
|
|
list a minimum of 8 action steps an instructor should take to enhance exercise adherence for a novice participant
|
|
Footwork
|
|
Discuss how exercises performed in water can help improve body weight, enhance cardiovascular system and prevent injuries
|
|
In water cost of energy is higher causing positive training results for cardio and weight management without fear or rough impact
|
|
What is the difference between land and water when it comes to exercise design
|
|
Running or walking in water provides a non impact cardio & strength training exercise in short time frame (quick)
|
|
State the difference between circuit and interval training methods
|
|
Circuit training- cardio & strengthening in short time frame aerobic training
strengthening and endurance, it works the aerobic and anaerobic systems ( 3 energy systems)
|
|
list and summarize the two circuit training formats
|
|
Super circuit: cardio-type station within the circuit of weight training exercises
|
|
What is work/active recovery ratio interval training
|
|
how much time is spent pushing hard then how much time recovering before repeating
Work ratio = high intensity portion of workout and Active recovery ratio = low intensity movement
|
|
What is work to recovery ratio when teaching interval training?
|
|
Work-to-recovery ratio: how long participants work and recover is dependent on their goals, fitness level and energy systems (aerobic vs anaerobic)
|
|
list a minimum of four things one should do to ensure they are riding properly (cycling)
|
|
-hands remain light on handlebars
|
|
list 3 things an instructor should consider when designing an indoor cycling class
|
|
- teaching off bike
|
|
For group exercises AFAA recommends a range between ____to ____ repetitions depending on whether the focus is muscular
|
|
8 - 12
|
|
list 4 muscles that tend to be weaker than their opposing groups
|
|
External shoulder rotators Lower trapezius
|
|
list 4 muscles that tend to be tight
|
|
Internal should
|
|
Discuss constant vs variable resistance and what form of equipment used in group exercise class would resemble variable resistance
|
|
Constant- dynamic resistance where its directed against target muscle (muscle group) (free weights) Dumb bells , medicine balls
|
|
list 7 action steps for designing a resistance tubing class
|
|
1-check tubes for holes
|
| list a minimum of 3 strength training sequences appropriate within the group exercise setting |
|
-arm combinations (bicep curl to overhead press)
|
|
list 7 principals of mat science
|
|
Balance
|
|
list 4 class format guidelines for MAT science
|
|
-always begin w warm up and breathing
-always finish w/ cool down relaxation period
|
|
what are guidelines for various participant step levels
|
|
Pre class instructions
Warm - up
Flexibility and Final Class
|
|
List the appropriate BPM for:
|
|
Warm up: 120-134 duration(8-12min)
(advanced) 128-135 duration (20-60min)
duration 15-20 min
|
|
List techniques for body alignment
|
|
Shoulders back, relaxed
|
|
List stepping techniques
|
|
use full body lean (do not bend)
|
|
How to prevent knee injury while stepping
|
|
-ROM of knee should be kept under 90 degree angle
|
|
What does EIA stand for and how can it be prevented
|
|
-exercise induced asthma or broncho spasm
have inhaler at all times, exercise intensity should start low to high, avoid exercising outside (cold/highpollen) exercise in humid areas (pools), breath through nose
|
|
List 6 exercise guidelines for participants with heart disease
|
|
- CVD participants should be screened (release form)
|
|
list 4 exercise guidelines for participants with arthritis
|
|
-low impact exercise should be encouraged
|
|
List 4 precautions that should be taken for diabetic participants who are attending a group exercise class
|
|
-blood glucose should be monitored
|
| list 8 exercise guide lines for a participant with hypertension |
|
1-emphasize cardio activity
8- teach relaxation and stress management techniques
|
|
No one rule necessarily applies to all large sized adults in terms of exercise precautions because ________
|
|
Each person is different
|
|
what is preferred method of monitoring exercise intensity in the older adult population and what is the appropriate range
|
|
cardio @ low to moderate pace
|
|
what method of resistance training would be appropriate for older adults with arthritis and osteoporosis
|
|
slow stretching, isometric exercises
|
|
list 2 methods of stretching that are recommended for older adults
|
|
static and slow dynamic
|
|
list at least 4 program design guidelines for the older adult
|
|
-participants should know how to monitor workload
|
|
List 3 exercise considerations during pregnancy
|
|
cardio changes- blood volume increases , causing increased demands
|
|
list 5 things a fitness professional should consider prior to working with pregnant women
|
|
1-goal is renewed energy -
|
|
list 3 exercise modalities that pregnant women can perform along with any risks and modifications that should be taken
|
|
-high impact to low impact
|
|
list 4 exercise recommendations outlined by USDHHS, ACSM
|
|
- 60 minutes of activity 3-4 days/week
|
|
list 3 general guidelines to resistance training in children and adolescents
|
|
-resistance training movements
|
|
list 3 special considerations regarding resistance training in children and adolescents
|
|
-activity should be appropriate and varied
|
|
discuss 4 way to ensure a successful substitute teaching experience
|
|
having consistent policies in place
|
|
list 7 service group exercise instructors should deliver in order to adhere to the standard of care outlined by the fitness industry
|
|
-screening
|
| List three physiological adaptations that occur to improve exercise performance? |
|
Increased maximal blood flow Increased O2 delivery and CO2 removal Increased maximal oxygen uptake and aerobic power |
| Excess Post-Pxygen Consumption (EPOC) |
| refers to oxygen uptake remaining elevated above resting levels for several minutes during exercise recovery |
| Oxygen Deficit |
| A period in which the level of Oxygen consumption is below what is necessary to supply appropriate ATP production required of any exercise |
| Anaerobic Threshold |
| The point at which the body can no longer meet its demand for Oxygen and anaerobic metabolism is accelerated |
|
Aerobic Capacity |
| The ability of the body to remove Oxygen from the air and transfer it through the lungs and blood to the working muscles; related to cardiorespiratory endurance |
| Lactic Acid |
| The by- product of anerobic metabolism of glucose or glycogen in muscle |
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference in the breakdown of glucose?
|
|
*Aerobic- complete breakdown of glucose
*Anaerobic- partial breakdown of glucose
|
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference in source of fuel
|
|
Aerobic- can use carbs, proteins, and fats as source of fuel
Anaerobic- can only use carbs
|
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference in duration of activities
|
|
Aerobic- Long-duration
Anaerobic- short-duration
|
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference with EPOC
|
|
Aerobic- smaller EPOC
Anaerobic- Larger EPOC |
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference in intensity
|
|
Aerobic- sub maximal work (moderate intensity)
Anaerobic- maximal output (high intensity) |
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference in usage of Oxygen for chemical breakdown
|
|
Aerobic- uses O2 for chemical breakdown
Anaerobic- doesn't need O2 for chemical breakdown
|
|
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic difference in by-products
|
|
Aerobic- CO2 and H2O are end products
Anaerobic- Lactic acid is the by-product
|
|
What is the average resting blood pressure of a healthy person?
|
|
120/80 mmHg
|
|
High Blood Pressure?
|
| 140/90 mmHg |
|
Pre hypertension
|
| 130/89 |

|
|
Pectoralis Major
|

|
| Deltoid |

|
| Biceps |

|
| Eternal oblique |

|
| Rectus Abdominis |
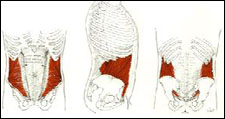
|
| Internal Oblique |

|
| Tensor Fasciae Latae |

|
| Addductors |

|
| Quadriceps group |
| Name the quadriceps goup |
|
Rectus Femoris Vastus laterlis Vastus Medialis Vastus Intermedius ( located under femoris) |
|
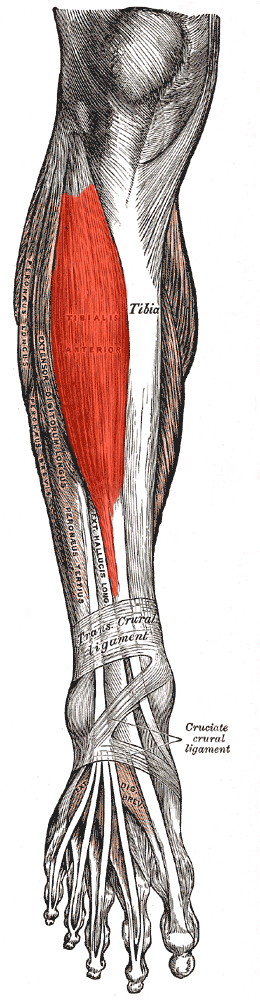
| Tibilas Anterior |

|
|
Quadratus Lumborum
|
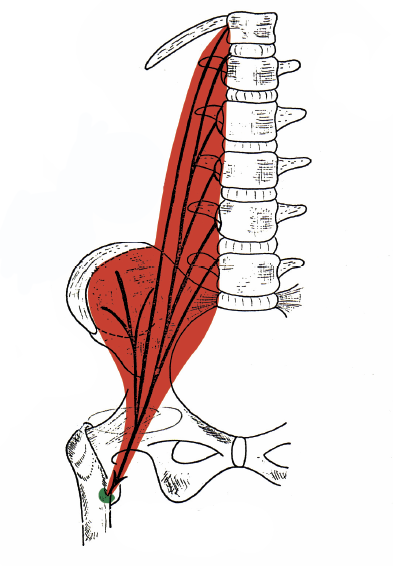
|
| Iliopsoas |
|
What two muscles are considered the hip flexor and the Lateral Spinal Flexor?
|
|
Lateral Spinal Flexor- Quadratus Lumborum
Hip Flexor- Iliopsoas
|

|
| triceps |

|
| Lattissimus Dorsi |

|
| Erector Spinae |

|
| Gluteus Maximus |

|
|
|
| isokinetic |
| Muscle contraction in which tension developes by the muscle while shortening at a constant speed is maximal over the full range of motion. |
|
Which 3 muscle contractions are used in a group exercise setting?
|
| Concentric, eccentric and isometric |
|
Musculoskeletal benefits of weight bearing activities
|
| increase bone density |
|
Musculoskeletal benefits of increased muscular strength
|
|
Increase both physical appearance and physical performance
|
|
Musculoskeletal benefits of increased muscular flexibility
|
|
improves tissues elasticity and helps facilitate movement
|
|
Define the stretch reflex, its purpose, and when it occurs
|
|
Muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle maintains a constantly length
|
| Explain why ballistic movements can be dangerous |
| The muscle spindles will sense quick changes in muscle length and cause muscular contraction |