|
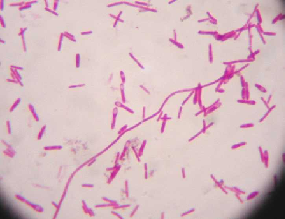
Bacillus |
|
Bacillus is a genus of rod-shaped bacteria.
Gram-positive organism.
(looks like funky coral)
|
|
Spirillum |
|
Spirillum in microbiology refers to a bacterium with a cell body that twists like a spiral.
Spirillum is a genus of gram-negative bacteria.
(Neon sign, black background with glowing bacteria.) |
|
Staphylococcus |
|
Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria. Under the microscope they appear round (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters.
(Blue, looks like color-blind test.) |
|
Streptococcus |
|
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria. They grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning easily bent or twisted, like a chain (twisted chain). Contrast this with staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes and generate grape-like clusters of cells.
(Blue.) |
|
Clostridium Tetani |
|
Clostridium tetani is a Gram positive rod-shaped bacterium.
Endospore
(Easter Grass, Swollen Ends) |
|
Amphitrichous Flagella |
|
Amphitrichous bacteria have a single flagellum on each of two opposite ends (only one flagellum operates at a time, allowing the bacteria to reverse course rapidly by switching which flagellum is active).
(Brown snakes) |
|
Peritrichous Flagella |
|
Peritrichous bacteria have flagella projecting in all directions.
(Brown furry) |
 Mycobacterium Tuberculosis |
|
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
M. tuberculosis is characterized by caseating granulomas containing Langhans giant cells, which have a "horseshoe" pattern of nuclei. Organisms are identified by their red color on acid-fast staining.
(Acid-fast stain - red/purple) Blood red |
|
Capsule Stain |
|
Capsule Stain
Stain background - Red Capsule - Unstained |
|
Ubiquity of Microbes - Microorganisms
They are everywhere. They are free-living and do not need a host.
They are commensal/mutualistic - they benefit/we benefit.
They can also be opportunistic pathogens - if conditions are right they multiply and cause harm. |
|
Germ Theory of Disease - theory that microorganisms cause disease.
Tryptic Soy Agar - (TSA) - Solid medium, food for bacteria.
Fomite - any inanimate object or substance capable of carrying infectious organisms (such as germs or parasites) and hence transferring them from one individual to another. |
|
Colony - each dot
Only takes one cell on nutrient medium to start growing/multiplying.
Eventually you can see an area of growth on the medium = colony.
Morphology - study of shape |
|
Every colony has a specific set of characteristics: Margin - entire(smooth), undulate/wavy, lobate, filamentous, rhizoid (branched) Elevations - flat, raised, convex, pulvinate (very convex), umbonate (raised in the center) Texture - moist, mucoid, dry Pigment - opaque, translucent, shiny, dull |
|
Stains are solutions consisting of a solvent and a dye.
Charged regions of the dye molecule that give color are termed chromophores.
Chromophores stain bacteria through bonds formed with the cell. Bacterial cell surfaces tend to have a - charge so a dye with a + chromophore will adhere to the cell.
|
|
Common stains - Methylene Blue, Crystal Violet, Safranin
Heat fixing has two important purposes: kills bacteria and coagulates cell proteins so they are more visible.
Cells are transparent and dyes make them visible. We can then see cell morphology and arrangement. |
|
Differential Stain - allows us to detect changes between organisms
2 stain process with de-colorization inbetween. Iodine added as mordant. Decolor (alcohol wash). Gram - will decolor. Gram + - keep color. |
|
Counterstain - safranin is applied and gram negative cells turn the color of this dye which is pink/red.
Gram - have more lipid content in cell wall. Alcohol forms holes in wall releasing CV in decolorization.
Decolorization of gram + does not make them porous so stain remains in cell.
Decolorization is most imp process of the gram stain. |
|
Poor technique and age can give false results.
Shapes of bacteria:
Bacillus - rod shaped Coccus - spherical shaped Spirillum - spiral shaped Staphylo - cluster arrangement Strepto - chain arrangement |
|
Acid fast prganisms have mycolic acid in cell wall.
Mycolic acid is a waxy substance that prevents true decolorization of primary stain.
Two methods employed for acid fast bacteria - Ziehl-Neelsen and Kinyoun methods. |
|
Primary stain in ZN method is Carbolfuschin (red).
Alcohol is used as a decolorizer in non-acid fast cells. Acid fast cells will not decolorize. After decolorizing, another stain is applied to those that lost the carbolfuschin stain. Methylene blue is used.
Acid fast=red. Non-acid fast=blue. |
|
Capsules are composed of mucoid polysaccharides that repel most stains. This area is hard to stain, so we stain everything else.
Congo red or nigrosin are commonly used to stain. |
|
Endospore - a dormant form of bacterium. Not all bacteria form endospores.
If a bacteria produces an endospore it means the conditions around it have deteriorated.
Spores resist heat as well as most chemicals.
Tough outer coating of a spore is made of keratin. |
|
Scaheffer-Fulton Method - primary stain is Malachite green which is forced into spore by heating. Counterstain is safranin.
Spores loacted according to the following: terminal, central, subterminal |
|
Hanging Drop - wet mount that is inverted on a depression slide.
Ring of petroleum jelly prevents evaporation of H2O and allows coverslip to adhere to depression slide.
Motility should not be confused with Brownian Motion. |
|
Ryu stain is used to see flagella on bacteria. It allows you to see the various arrangements of the flagella.
Montrichous Amphitrichous - both ends Lophotrichous - tufts at both ends Peritrichous - flagella all over |
|
Gram Stain after Heat Fix
1-Cover smear with crystal violet stain for 1 minute. 2-Rinse with distilled H2O. 3-Cover Smear with iodine for 1 minute. 4-Rinse with distilled H2O. 5-Decolorize with alcohol until run-off is clear. 6-Rinse with distilled H2O. 7-Counterstain with safranin for 1 minute. 8-Rinse with distilled H2O. |
|
9-Gently blot dry in biulous paper.
Observe under oil immersion. |