| Zeitgeist |
| The spirit of the times or the many factors of an era that influence the clothing styles. |
| As Fashion Changes..... so does |
|
figure emphasis e.g. bosom, genitals, waist pose patterns e.g. debutante slouch movement e.g. hobble skirt |
| Why Clothing Varies |
|
1. differences in purpose for wearing clothes 2. differences in materials available for making clothes 3. difference in ways of making clothes 4. differences in clothing customs 5. social and political influences |
| Draped clothing |
| Created through the arrangement of material around the body. It may be pinned, pleated, draped and belted in different ways. This tended to be common in warmer climates |
| Tailored clothing |
| Is cut, sewn and shaped. Generally, these were warmer clothes and were more common/necessary in colder climates |
| The basic garments of the ages |
| loincloth, skirt, tunic, cape |
| Prehistoric Clothing |
|
~Silhouette - rectangular ~Unfitted coverings made of animal furs and hides, plant materials (bark cloth), also felted wool. ~at first it was just draped and tied (belted) |
| Prehistoric Yarn |
| was made from threadlike parts of plants or from fur or the hair of animals. Also, sinew. Later, it was made from cotton or wool |
| Sewing began... |
| sewing began probably around 30,000 BC, when bone needles were developed. |
| Tunic |
| this garment was made of a length of woven material or animal skin. It was typically folded in half, sewn up the sides with a slit for a neck opening. |
| Loincloth |
| This was made of cloth or fur and designed to cover the genital areas. |
| Cape |
| This was a piece of fabric or fur, thrown or arranged around the shoulders. |
| Girdle |
| This was a tie or belt-like article worn to support and/or arrange the design of the garment. It was also used for utilitarian purposes, e.g. to hold a knife. Often the girdle could be very decorative. |
|
Ancient Egypt Time & Location |
|
~5,000 B.C. - 332 B.C. ~period ended when Alexander the Great conquered Egypt in 332 B.C. ~located in the NE corner of Africa, centering around the Nile River in a valley with cliffs and desert ~ Mediterranean Area |
|
Ancient Egypt Social Structure |
|
A. Theocracy B. Pharaoh ~Dynasties & kingdoms A. Classes were divided as follows: (compare this to a pyramid) 1. royalty, priests and nobles 2. scribes (managers, bureaucrats) 3. artisans, craft workers and merchants 4. workers 5. slaves (foreign captives) |
|
Ancient Egypt Economy & Commerce |
|
~Agriculture, Manufacturing, Craftsman, Mining ~Exports/Imports: Barter system |
|
Ancient Egypt Religion |
|
Pharaoh Afterlife Re and Osiris |
|
Ancient Egypt Literature and Art |
|
~The Book of the Dead ~Paintings ~Sculpture - statues e.g. sphinx ~Painting ~Architecture -pyramids, temples,tombs, palaces and homes of the upper class. |
|
Ancient Egypt Intellectual |
|
hieroglyphics papyrus (paper made from the reeds along the nile) astronomy medicine math |
| Egyptian Motifs |
|
the scarab the hawk, the cobra the vulture (Upper Egypt) The Eye of Horus |
| Egyptian Clothing Creation |
|
Linen , a very fine see-through fabric from flax plant Other fibers Colors Embellishments Goffering (similar to ironed pleats) |
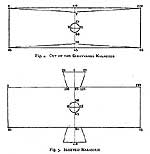
| Egyptian Silhouette |
|
Tubular or Triangular. Draping |
| Egypt body culture |
|
body conscious cleanliness. Cones of scented wax were set on the heads of guests at parties, and as the evening progressed, the wax would melt over the wigs and perfume the air with myrrh or cinnamon. (Tortora: 24 ) Cosmetics e.g. Kohl Jewelry and head dresses e.g. Jeweled Collars |

|
|
Shenti Egyptian "skirt" for males worn multiple ways. Often goffered.
|

|
|
shendot Egyptian. Strip of hanging fabric worn by males to indicate status & manhood |

|
|
Egyptian. sheath gown
|
|
|
kalasiris Egyptian. Tunic-like
|
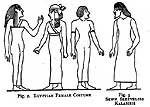
|
|
procardium Egyptian. "tunic" for females. Often worn below breasts with "suspender" straps.
|
| Goffering |
| Egyptian pleating. |

|
|
Gala Gown or Gala Skirt. Egyptian. Male or female.
|

|
|
postiche Egyptian. Fake goatee held on by straps. |
| Ancient Mesopotamia Time & Location |
| ~5,000 B.C. - 539 B.C. ~The period ended with the takeover by the Persians in 539 B.C ~Located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in the part of the world that today forms much of the mideast. (Iraq, eastern Syria and SE Turkey). Surrounded by desert. |
|
Ancient Mesopotamia Groups of people |
|
1. Sumerian (cultural), 2. Babylonian (not much progress), 3. Assyrian (Military) and 4. Chaldean or Neo-Babylonia (restored some of the culture). King Hammurabi (Babylonian) and Nebuchadnezzar (Chaldean) |
|
Ancient Mesopotamia Social Classes |
|
Classes were divided as follows: 1. Patricians or aristocrats (land holders) 2. Burghers or common citizens 3. serfs (own land) and slaves |
|
Ancient Mesopotamia Economy |
|
Agriculture Chief Products Barter System for Imports & Exports |
|
Ancient Mesopotamia Religion |
| Polytheistic Sha-Mash and Ishtar present world belief |
|
Ancient Mesopotamia Literature/Art |
|
Depicted scenes of daily life and events around them. Ziggurat Royal Standard of Ur Used cylinders to imprint motifs on tiles. |
|
Ancient Mesopotamia Intellectual |
|
Cuneiform Commerce related systems Law Water clock and lunar calendar - Math - used in building, area, volume, etc. Astronomy Medicine Personalitites Sumerian - Sargon I Babylonians - Hammurabi (Code of Hammurabi) Assyrians - Ashurbanipal Chaldeans - Nebuchadnezzar (built the terraced roof known as the Hanging Gardens ,one of the 7 wonders of the world). |
| Mesopotamian Clothing |
|
Plant-life motifs and geometrics. Motifs were used on fabrics. Wool Cotton Linen and Silk through trade |
| Mesopotamian Silhouette |
|
Tubular or Triangular (through tiering). Fringing Draping |
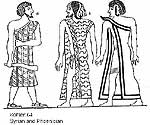
|
|
Syrian and Phoenician Cape/Wraps a meld of Egyptian and Asian |

|
|
Kuanakes Sumerian: Men and Women |
| Sumerian: Men and Women |
| Tunic, Skirt, Capes, Girdles, Belts Men were clean shaven but wore beads |

|
|
Assyrians and Babylonians Clothing Tunic or Candys |
| Persians |
| War-fare, militaristic, hunters and horsemen. These were the first people to cut and sew clothing (as opposed to drape) Anaxiride - trousers tightly fitted at the ankles. |
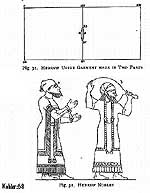
|
|
Ephod Hebrew. Pancho-like overgarment |

|
|
Aba Hebrew. Hood/viel |

|
|
caftan Hebrew tunic/dress. Loose flowing. |
| Mesopotamian hats |
| Turbans Assyrians= brimless hat |
| Mesopotamian Hair |
| Assyrian= small curls |
| Ancient Crete and the Aegean |
|
~Time Period: 3000 - 1400 B.C. ~An island off the coast of Greece, in the Mediterranean Sea ~Minoan (Crete), Helladic Mycenaeans (mainland), Cycladic (islands) and Troadic (Troy) ~The Aegean Sea, Crete |
|
Ancient Crete and the Aegean Clothing |
|
Plant-life motifs and geometrics. Motifs were used on fabrics. Wool Cotton Linen and Silk through trade Metal and Leather |
|
Ancient Crete and the Aegean Silhouette |
| Tubular or Triangular (through tiering). |
| bolero jacket |
| Crete/Aegean. The shrunken jacket (as worn by snake goddess statue). Exposed breast & mid-length sleeves. |

|
|
Creten & Aegean Skirt/Tunic/girdle
Women wore multi-tiered skirts, double sided apron & a girdle/belt. |
|
Ancient Greece Time/location |
|
~Time Period: 3,000 B.C. - 323 B.C. ~This period extended from the Aegean civilizations through Hellenic Greece (there are many periods, each given names, Homeric, Dark Ages, Hellenic, etc.) ~Greece is located on the Mediterranean Sea which sits to the south. The Aegean Sea is on the east side, between Greece's mainland and Asia Minor. The country is composed of a mainland and various islands ~ ~ |
|
Ancient Greece Culture/Social |
|
peace loving beauty of the body belief in equality of man Classes were divided as follows: * the Citizens * the Metics * Slaves |
|
Ancient Greece Economy |
|
Agriculture Industry Trade- Import/export |
|
Ancient Greece Literature and Art |
|
Homer's Epic poems, the Odyssey and the Iliad Tragic Drama Art - Statues Pottery Architecture - Doric: rather heavy, sharply fluted columns, and Ionic: more slender, graceful columns |
|
Ancient Greece Intellectual |
|
Olympic Games - Philosophy of Thought - Math - Biology - Math - Medicine - |
|
Ancient Greece Wars/periods |
|
1. Persian War, 479 - 439 B.C. 2. Peloponnesian War, 431 - 404 BC Athens vs. Sparta 3. Rise of Macedonia and Alexander the Great 404 - 323 B.C. 4. Hellenistic Age, 323 BC to 31 BC |
| Ancient Greek Clothing |
|
A. Motifs Greek Key Geometric Plant life B. Materials Spinning and weaving Wool and linen purpura shellfish. Other Information simple design use of draping |
| Ancient Greek Silhouette |
| Ancient Greek Clothing |

|
|
Chiton The tunic of Greek women. Long draped dress tied at shoulder w/ fibula (pins). Doric= 1 pin; Ionic= multiple pins along arms (more detailed architecture too) |
| fibula |
| Pins (looked like safety pins). |

|
|
chlamys Greek. Cape draped around shoulder and open at "sword arm" |

|
|
Greek girdle
Women. Wrapped/tied around waist and breasts |

|
|
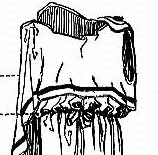
himation
Greek. Man or woman. Piece of rectangular cloth draped over shoulders/head as a hood/viel. (Draped like a scarf, not tied like medieval veil.) |
|
|
peplos
Greek. Overgarment shirt. Rectangle cloth pinned at shoulders & open on one side. |

|
|
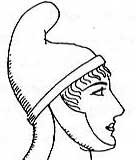
petasos
Greek. Brimmed hat (like straw hat) |
|
|
Phrygian Cap
Greek. Strapped on cap with curl @ top. "Liberty Cap" |

|
|
tholia
Greek hat. Looks like a witch hat that is balanced/pinned on head. |
| tiara/stephane |
| Greek. Evolved into metal crown. |
|
|
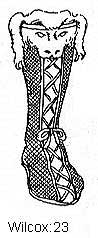
Buskin
Greek boot made of fur wrapped and tied around foot. |
| Ancient Rome Time/Location |
| ~Time Period: 12th C. BC to 476 AD ~Tiber river ~Its history is divided into Early Inhabitants (till 6th C) the Republic (6th C - 27 BC) and the Roman Empire (27 BC to 476 AD). |
|
Ancient Rome Social |
|
Classes were divided as follows: 1. Citizens - ( the patricians, plebeians and citizens without the vote) 2. the rest of the population - slaves and non-citizen foreigners. Women became educated and important in the running of daily affairs. the paterfamilias. Citizenship Emperor was the top of the social structure |
|
Ancient Rome Economy |
|
Agriculture was the #1 economic activity. Warfare was the other. As Rome conquered countries it set up plantation farming. Trade extended to all parts of the known world, e.g. India, China. Manufacturing of pottery, textiles, metal and glass. Agriculture |
|
Ancient Rome Religion |
|
Religion was Polytheistic Their Gods and Goddesses resembled Greek gods, but were not quite as human. Stoicism |
|
Ancient Rome Literature and Art |
|
Literature was very related to philosophy. Horace and Virgil were two philosopher/writers. Art - influenced by the Greeks. Became more original in the Empire period. Architecture Sculpture, Fresco |
| Ancient Rome Clothing |
|
A. Motifs many types of motifs decorations were embroidered, woven B. Materials Weaving, spinning etc. was carried out in business establishments, rather than the home... 50 - 100 people. (although some was performed in the home by the women) Wool, then linen were the primary fibers. Silk and Cotton Dyeing use of draping Indutus - garments that were 'put on'. Amictus - garment that were wrapped |
| Ancient Rome Silhouette |
|
Rectangular Draping |

|
|
Tebenna (Etruscan) (ta' ben-a)
Roman. Draped/Wrapped Hood. |

|
|
Tunic (Men), Tunica (Women)
Roman. |

|
|
Stola
Roman. Overgarment. Woman. Rectangular cloth draped over shoulders and wrapped around body. |
| Clavus (plural) Clavi (singular) |
|
Roman. Stripe down front of clothing for status.
|

|
|
Dalmatica
Roman. Male Overgarment. Tunic with sleeves, but not wrapped like tunic/tunica. |

|
|
Toga
Roman. Made from Rectangular cloth wrapped around body. |

|
|
Palla - (Women)
Roman. Woman. Rectangular cloth drapedover 1 shoulder and wrapped around body once. Could be pulled over head as a hood for modesty. |

|
|
Paludeamentum (pa-lu-da-men'-tum)
Roman. Male. Cape draped over one should. Similar to Greek chlamys. |

|
|
Paenula - (pie-new'-la)
Roman. Male. Semi-circle cloth draped around shoulders & could be used as a hood. |
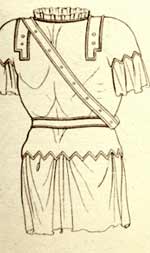
| Strophium - Women |
| Roman. bra |
| Pagne |
| Roman. Women's underwear/swimwear. |
|
|
Cuirass
Roman. Armor Breastplate |
| diadem |
| Roman. Headband/crown. |

|
|
Calceus
Roman footwear. Sandal-like w/ open toes. |
| Byzantine Time/Location |
| ~Time Period: 330 AD to 1453 AD ~Constantinople is located at the entrance of the Black Sea, and it became the focal point of many trade routes between the East and West. Thus, it became a metroplolis and the focal city of Europe until 1200. The influences of east and west became intermixed. Byzantium was constantly at war Crusaders sacked the city in 1204 and destroyed much of its art and culture. |
|
Byzantine Religion |
|
~Religion was Christianity, split from Roman Catholic Church = Eastern Orthodox ~Christianity spread within the Roman Empire between the 1st and 4th centuries AD Why? Romans opposed Christianity Christianity in Western Europe was centered in Rome, with the Roman Catholic Church (Pope or Bishop). An Eastern Europe the Greek Orthodox Church (Patriarch) centered in Constantinople. These two powers vied for control, and in 1054 the church split to become two entities. |
|
Byzantine Social |
|
The head of the state was the Byzantine Emperor. The class of nobility became the main force of government. |
|
Byzantine Economy |
|
Trade Development of silk production and woven fabrics Silk production Manufactured patterned fabrics, damasks, brocades, etc. |
|
Byzantine Literature and Art |
| Mosaics |
| Byzantine Clothing |
|
Many of Persian influence, as well as Eastern influence. Decorations were embroidered, woven. Two major contributions to the world were: 1. Development of patterned woven fabrics, (using a shuttle), e.g. brocade and damask 2. establishment of a silk industry. Wool and linen were the primary fibers. Fabrics were adorned with semi-precious stones, enamel medallions, embroidery and appliqués. D. Other Information more fitting patterned fabrics layering |
| Byzantine silhouette |
|
Early silhouette - Roman influence Later silhouette - more fitted, with influence of the Orient. |

|
|
Tunic/Gunna
Byzantine. Gunna=Female. Fitted. Looks pre-medieval. |
 
|
|
Dalmatique/Dalmatica
Byzantine. Female. Decorated, loose, long-sleeve tunic. (like kimono.) |

|
|
Juppe
Byzantine. Sewn shirt with baggy sleeves in under arms. |
| Paludamentum/Mantle |
| Byzantine. Male= cape like greek/roman. Female= wrapped around shoulders. |
| Tablion |
| Byzantine. Patch sewn usually onto the Paludamentum/Mantle |
| Segmentae |
| Byzantine. Design/patch sewn onto tunic/clothing. |
| Trousers |
| Byzantine. fitted pants for men. |
| Lorum |
| Byzantine. Male. Long, rectangle strip of fabric wrapped around body in an X pattern. |
| Clavus (Byzantine) |
| Similar to Roman status stripe, but now more decorative and not only for status. |
| Byzantine headwear |
| Veils, Turban-like Headwear, Diadem Crowns |
| Byzantine Hair |
|
Clean-shaven men Women, soft flowing wavy hair, parted in center, or pulled back. |
| samples |
| Byzantine Footwear. Open sandal or wrapped sandal. |
|
Middle Ages (Medieval) Time/Location |
|
~Time Period: approx. mid 5th C. to 1500 ~About 1000 yrs between Roman Empire & Renaissance. ~All countries of Western Europe at that time. e.g. Italy, France, England, Spain, Germany, Portugal, Netherlands, etc. ~Feudalism Islam Dark Ages vs. Later Middle Ages, Charlemagne |
|
Middle Ages Social |
|
Social Structure: Nobles (land holders) and Serfs (masses) King - Powerful Lords- Lessor Lords, Knights, Serfs |
|
Middle Ages Economy |
|
Feudal System The Crusades By approx. 10th C trade increased and towns began to grow. Bourgeoisie or townspeople. - a new Middle Class Trade Fairs Merchant Guilds By 13th C. the church owned 30% of the land in Western Europe. In early Middle Ages, the decline of Trade and Industry... merchants stopped shipping, roads deteriorated. In general, as feudalism increased, trade decreased. |
|
Middle Ages Religion |
|
Two major religions: Christianity (2 orders) and the Moslem's Islam (Mohammed the prophet, and Allah their God). Crusades: 1095 - 1291, the Holy Wars - between the Christians and Moslems. Holy Inquisitions |
|
Middle Ages Literature and Art |
|
Latin became broken down into local languages, e.g. French, Italian and Spanish in the making. The Church preserved Roman-Greco culture (copying books and manuscripts), and influenced literature with religious themes and architecture (cathedrals) Music - Gregorian Chant Architecture was first Romanesque (thick walls, few windows, rounded arches) and later Gothic (thin walls, pointed arches, tall spires, gargoyles, stained glass) e.g. Notre Dame and Westminster Abbey. |
|
Middle Ages Intellectual |
|
Universities were founded, e.g. Oxford, Cambridge Invented magnifying lenses, glass windows, mechanical clocks. |
| Middle Ages Clothing |
|
A. Motifs many types of motifs decorations were embroidered, woven Cotton. New Fabrics were muslin, dimity, and silk damask. Trade Guilds were established to develop the manufacture of cloth for export. Wool |
| Middle Ages silhouette |
|
~Early silhouette was based on Roman influence, with simple cuts and styles. ~Later silhouette became more fitted. Fitting was achieved not only by 'cut' but by lacing of garments. |
| Gonelle/Cottelle/Bliaud/Bliaut/Gunna |
| Tunic of Middle Ages. Roman influence. |
| Kirtle/Chainse/Chemise |
| Middle Ages. Female loose dress. Not wrapped. |
| Cotehardie |
| Middle Ages female. 1st version of the signature dress of the era. |
| Surcoat |
| Middle Ages. Male/Female. Sleeveless tunic overgarment. |
| Houppelande |
| Middle Ages. Male. Coat/tunic over-garment. Typically knee-length. Belted for a false belly or not belted (as in marriage painting). |
| Tippet |
| Middle Ages. Long sleeves. Wealth symbol. |
| Doublet/Pourpoint/Joupon |
| Middle Ages. Male. Shirt barely long enough to cover butt. Usually warn w/ belt (to make short skirt shape) & pants. |
| Chainmail |
| Middle Ages |
| Braies |
| Middle Ages. Male underwear that went to knees. Made by wrapping & tying. |
| Chausses |
| Middle Ages. Male. Hose/trousers. Could be knee-high or pants. |
| Camise or Shert |
| Middle Ages. Loose shirt with pleats/scrunching around or below neckline. (like a short night shirt.) |
| Chaperon |
| Middle Ages. Hood. |
| Liripipe |
| Middle Ages. Long strip of fabric hanging from top of hood or cap. (Night cap inspiration) |
| Parti-color |
| Middle Ages. garment that is 2 colors (half & half). Known as Jester's clothing. |
| Coif |
| Middle Ages. Skull cap |
| Wimple/Gorget |
| Middle ages. Female. Wrapped around headdress. |
| Toque |
| Middles Ages. Female headwear. Open, crown-like hat. Often held on by chinstrap. |
| Escoffion |
| Middle AGes. Female. Double-horned headdress |
| Hennin |
| Middle AGes. Single horned headdress |
| Caul/Reticulated Headdress |
| Middle Ages. Female. Wrapped around braid and worn on both side of head. |
| Poulaine/Cracow |
| Middle Ages. Male shoes. Very pointed. |
| Pattens |
| Middle Ages. Strapped onto shoes to walk through mud |
| Chopines |
| Middle Ages. Platform heels. |

|
| Egyptian sandals |
