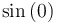
|
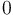
|
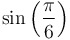
|
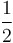
|
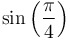
|
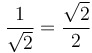
|
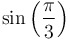
|
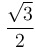
|
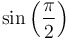
|
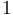
|
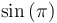
|
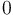
|
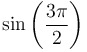
|
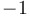
|
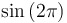
|
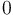
|
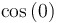
|
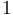
|
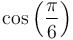
|
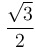
|
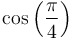
|
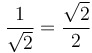
|
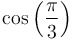
|
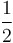
|
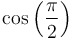
|
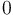
|
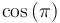
|
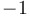
|
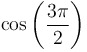
|
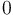
|
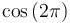
|
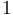
|
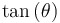 (in terms of sine and/or cosine) |
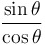
|
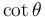 (in terms of sine and/or cosine) |
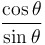
|
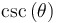 (in terms of sine and/or cosine) |
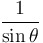
|
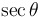 (in terms of sine and/or cosine) |
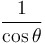
|

|
Graph of 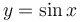
|

|
Graph of 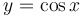
|

|
Graph of 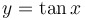
|

|
Graph of 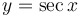
|

|
Graph of 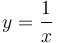
|

|
Graph of 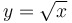
|

|
Graph of 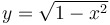
|

|
Graph of 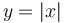
|

|
Graph of 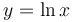
|

|
Graph of 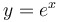
|
|
Definition: An even function is... |
...symmetric with respect to the 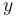 -axis, like -axis, like 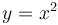 , , 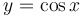 , or , or 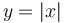 . .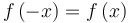
|
|
Definition: An odd function is... |
...symmetric with respect to the origin, like 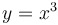 , , 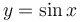 , or , or 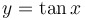 . .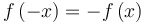
|
| Two formulas for the area of a triangle |
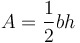 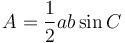
|
| Formula for the area of a circle |
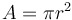
|
| Formula for the circumference of a circle |
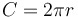
|
| Formula for the volume of a cylinder |
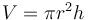
|
| Formula for the volume of a cone |
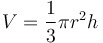
|
| Formula for the volume of a sphere |
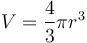
|
| Formula for the surface area of a sphere |
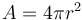
|
| Point-slope form of a linear equation |
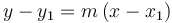
|
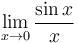
|
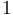
|
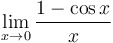
|
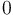
|
|
Definition: A tangent line is... |
| ...the line through a point on a curve with slope equal to the slope of the curve at that point. |
|
Definition: A secant line is... |
| ...the line connecting two points on a curve. |
|
Definition: A normal line is... |
| ...the line perpendicular to the the tangent line at the point of tangency. |
Definition: is continuous at is continuous at  when... when...
|
1. 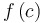 exists; exists;2. 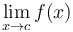 exists; and exists; and3. 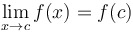 . .
|
Limit definition of the derivative of  : :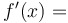
|
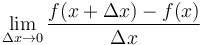
|
Alternate definition of derivative of  at at  : :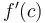 = =
|
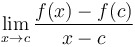
|
What 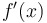 tells you about a function tells you about a function
|
|
• slope of a curve at a point • slope of tangent line • instantaneous rate of change |
|
Definition: Average rate of change is... |
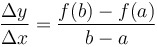
|
Power rule for derivatives: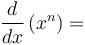
|
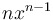
|
Product rule for derivatives: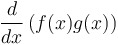 = =
|
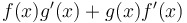 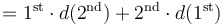
|
Quotient rule for derivatives: 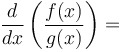
|
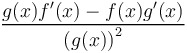 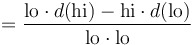
|
Chain rule for derivatives: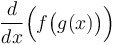 = =
|
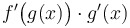 , or , orderivative of the outside function times derivative of the inside function |
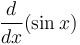 = =
|
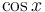
|
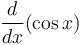 = =
|
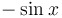
|
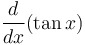 = =
|
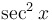
|
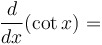
|
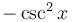
|
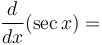
|
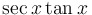
|
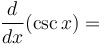
|
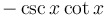
|
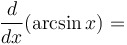
|
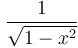
|
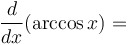
|
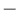 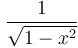
|
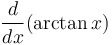 = =
|
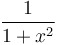
|
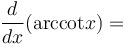
|
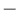 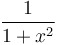
|
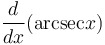
|
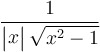
|
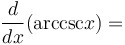
|
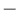 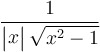
|
Derivative of natural log: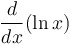
|
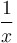
|
Derivative of log base 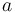 : :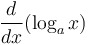
|
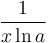
|
Derivative of natural exponential function: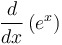 = =
|
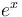
|
Derivative of exponential function of any base: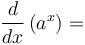
|
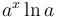
|
Derivative of an inverse function: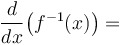
|
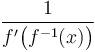 The derivatives of inverse functions are reciprocals. |
Rolle's Theorem:
If  is continuous on is continuous on 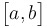 , differentiable on , differentiable on 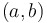 , and... , and...
|
...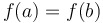 , then there exists a value of , then there exists a value of 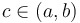 such that such that 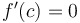 . .
|
|
Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: If  is continuous on is continuous on 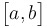 and differentiable on and differentiable on 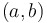 , then... , then...
|
...there exists a value of 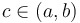 such that such that 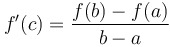 . .
|
|
Extreme Value Theorem: If  is continuous on a closed interval, then... is continuous on a closed interval, then...
|
... must have both an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum on the interval. must have both an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum on the interval.
|
|
Intermediate Value Theorem: If  is continuous on is continuous on 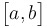 , then... , then...
|
... must take on every must take on every 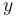 -value between -value between 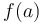 and and 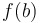 . .
|
| If a function is differentiable at a point, then... |
|
...it must be continuous at that point. (Differentiability implies continuity.) |
| Four ways in which a function can fail to be differentiable at a point |
|
•Discontinuity •Corner •Cusp •Vertical tangent line |
|
Definition: A critical number (a.k.a. critical point or critical value) of  is... is...
|
...a value of 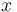 in the domain of in the domain of  at which either at which either 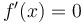 or or 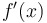 does not exist. does not exist.
|
If 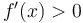 , then... , then...
|
... is increasing. is increasing.
|
If 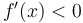 , then... , then...
|
... is decreasing, is decreasing,
|
If 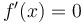 , then... , then...
|
... has a horizontal tangent. has a horizontal tangent.
|
Definition: is concave up when... is concave up when...
|
...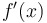 is increasing. is increasing.
|
Definition: is concave down when... is concave down when...
|
...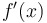 is decreasing. is decreasing.
|
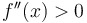 means that means that  is... is...
|
|
concave up (like a cup). |
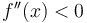 means that means that  is... is...
|
|
concave down (like a frown). |
|
Definition: A point of inflection is a point on the curve where... |
| ...concavity changes. |
| To find a point of inflection,… |
… look for where 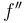 changes signs, or, equivalently, where changes signs, or, equivalently, where 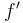 changes direction. changes direction.
|
| To find extreme values of a function, look for where… |
… 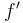 is zero or undefined (critical numbers). is zero or undefined (critical numbers).
|
| At a maximum, the value of the derivative… |
… 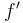 changes from positive to negative. changes from positive to negative.(First Derivative Test) |
| At a minimum, the value of the derivative… |
… 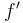 changes from negative to positive. changes from negative to positive. (First Derivative Test) |
|
The Second Derivative Test: If 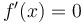 … …
|
…and 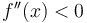 , then , then 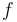 has a maximum; if has a maximum; if 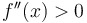 , then , then 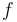 has a minimum. has a minimum.
|
Position function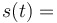
|
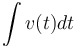 , the antiderivative of velocity , the antiderivative of velocity
|
Velocity function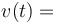
|
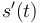 , the derivative of position, as well as , the derivative of position, as well as 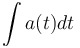 , the antiderivative of acceleration , the antiderivative of acceleration
|
Acceleration function 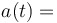
|
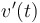 , the derivative of velocity, as well as , the derivative of velocity, as well as 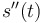 , the second derivative of position , the second derivative of position
|
| A particle is moving to the left when… |
…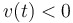 . .
|
| A particle is moving to the right when… |
…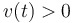 . .
|
| A particle is not moving (at rest) when… |
…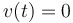 . .
|
| A particle changes direction when… |
…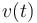 changes signs. changes signs.
|
To find displacement of a particle with velocity 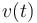 from from 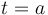 to to 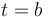 , calculate this: , calculate this:
|
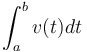
|
To find total distance traveled by a particle with velocity 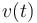 from rom from rom 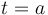 to to 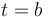 , calculate this: , calculate this:
|
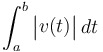
|
| Area between curves |
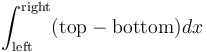
|
| Volume of a solid with cross-sections of a specified shape |
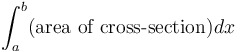
|
| Volume using discs |
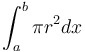 "perpendiscular" |
|
Volume using washers (discs with holes) |
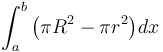
|
| Volume using shells |
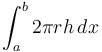 "parashell" |
| Area of a trapezoid |
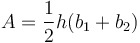
|
Trapezoidal rule for approximating 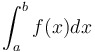
|
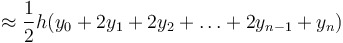
|
Average value of  on on 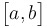
|
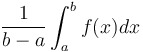
|
Power rule for antiderivatives: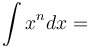
|
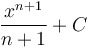 (for 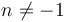 ) )
|
Constant multiple rule for antiderivatives: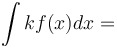
|
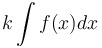 (A constant coefficient can be brought outside.) |
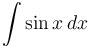 = =
|
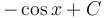
|
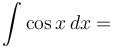
|
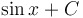
|
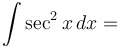
|
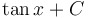
|
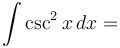
|
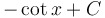
|
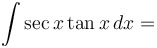
|
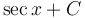
|
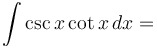
|
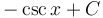
|
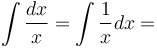
|
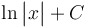
|
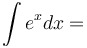
|
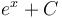
|
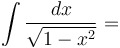
|
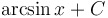
|
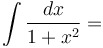
|
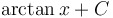
|
|
L'Hôpital's rule for indeterminate limits If 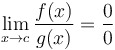 or or 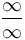 , ,
|
then 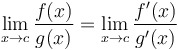 , if the new limit exists. , if the new limit exists.
|
|
Mean Value Theorem for Integration: If  is continuous on is continuous on 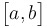 , then... , then...
|
...there exists a value of 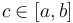 such that such that 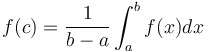 . .
|
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (part 1)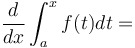
|

|
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (part 2)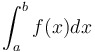 = =
|
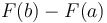 , where , where 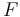 is an antiderivative of is an antiderivative of 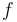
|
| A differential equation is... |
| …an equation containing one or more derivatives. |
| To solve a differential equation,... |
| ...first separate the variables (if needed) by multiplying or dividing, then integrate both sides. |
|
Exponential Growth and Decay: If 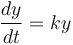 , then... , then...
|
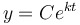 , where , where 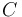 is the quantity at is the quantity at 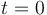 , and , and 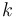 is the constant of proportionality. is the constant of proportionality.
|
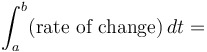
|
the amount which that quantity has changed from 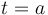 to to 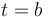
|